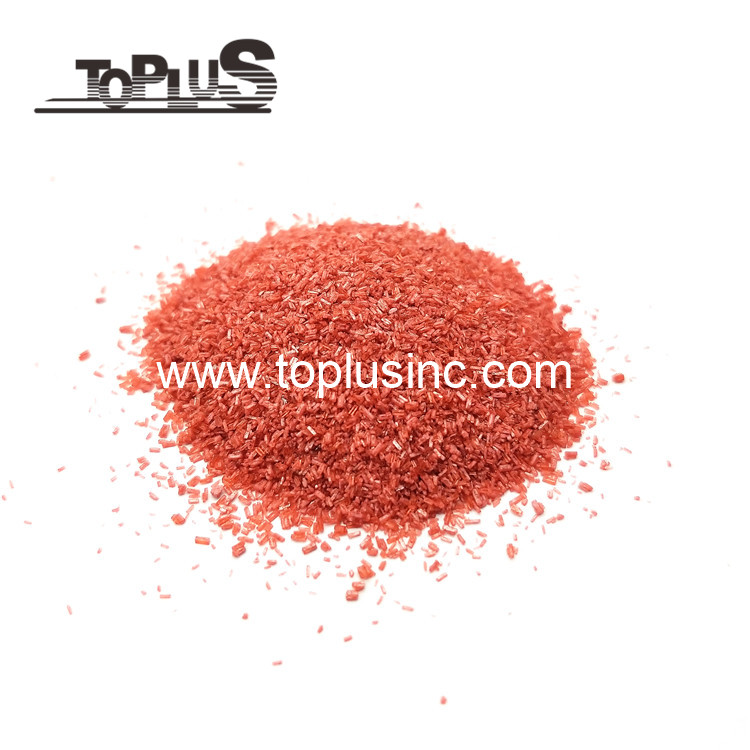
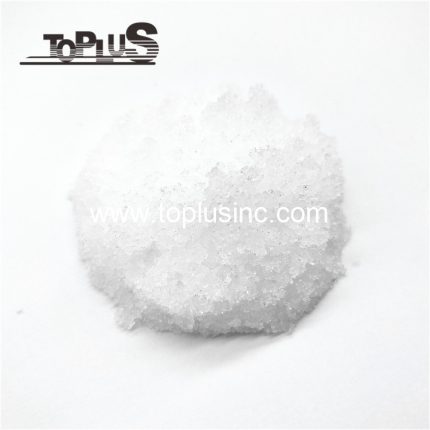
Catalyst Use Cobalt Acetate
PRODUCT DESCRIPTION
Molecular Formula:
(CH3COO)2CoPurity:
23.5%minCas No.:
71-48-7Einecs No.:
200-755-8Synonym:
Cobalt Acetate, Cobalt(II) Acetate, Cobaltous Acetate, Acetic Acid, etc.Images:
Description
Cobalt(ii) Acetate is soluble in acid and ethanol. The Cobalt Acetate molecular weight is 177.02. (CH3COO)2Co is an inert compound that facilitates various chemical reactions. Because of its good heat resistance, it releases a large amount of energy correspondingly when the temperature rises. Therefore, understanding the thermal decomposition mechanism of Cobalt Acetate has important theoretical significance and application value.
There are two main thermal decomposition mechanisms of Cobalt Acetate. One is to oxidize Cobalt Acetate to form acetic acid, carbon oxides, and hydrogen through a catalyst. The other is decomposing Cobalt Acetate into carbon dioxide, methanol, and other organic compounds at high temperatures.
First, Cobalt Acetate (power) will react with the oxidant to partially oxidize it into acetic acid, carbon dioxide, etc. The heat released at different temperatures is different. The higher the temperature, the more heat is released, which leads to a faster thermal reaction. This reaction process will go through four steps: oxidation, alkylation, stripping, and Methanol reduction. And each step of the reaction process will emit a certain amount of heat. And the temperature conditions of each step of the reaction are also different. Finally, the cobalt acetate system can also react at low temperatures. That is, thermal decomposition can also be realized by low-temperature catalysis.
Researchers are looking for a cobalt catalyst that can thermally decompose Cobalt Acetate at a temperature lower than average temperature. Thereby making the whole reaction process more straightforward and safer.
In summary, the thermal decomposition mechanism of Cobalt(ii) Acetate is as above. During this decomposition process, Cobalt Acetate will undergo reactions such as oxidation, alkylation, stripping, and methanol reduction, and each step of the response will correspond to different temperature conditions. Cobalt Acetate releases a large amount of energy correspondingly when the temperature rises.
Request a Quote
Download product spec
I consent to the processing of personal data and agree with the user agreement and privacy policy
 Agricultural Materials
Agricultural Materials Ceramics Materials
Ceramics Materials Electronic Materials
Electronic Materials Metallurgy Materials
Metallurgy Materials New Energy Materials
New Energy Materials Petrochemical Materials
Petrochemical Materials Surface Treatment
Surface Treatment
































